A nationwide study of primary biliary cholangitis prevalence, geographic distribution, and health care providers
August 2024
Abstract
Background: Prevalence estimates of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) in the United States have evolved with the introduction of newer real-world data capture approaches. Little is known about the geographic distribution of PBC in the United States and the health care provider (HCP) landscape for patients with PBC. This real-world study aimed to estimate the prevalence of PBC in the United States, assess regional variability in its prevalence, and describe HCPs for patients with PBC.
Methods: Patients with PBC were identified using Komodo's Healthcare Map, a large national administrative claims database. PBC prevalence per 100,000 adults was adjusted by age and gender at the 3-digit ZIP Code tabulation area level. Patients’ PBC-related medical or pharmacy claims were used to determine HCP specialties and affiliations (academic vs.nonacademic); the latest claim and all claims were examined.
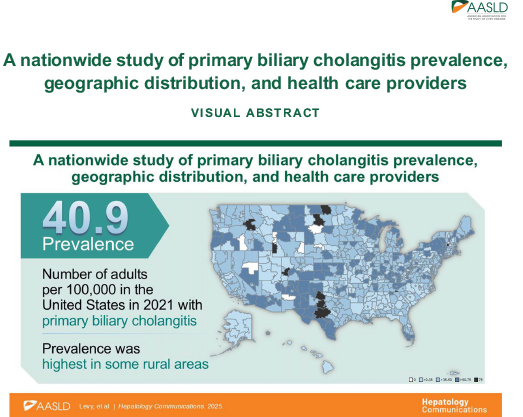
Results: The adjusted 2021 PBC prevalence was 40.9 per 100,000 adults.The highest absolute number of patients with PBC in the United States was in heavily populated urban areas, but prevalence adjusted for population size was highest in some rural areas. Among all claims, most (83.2%) patients received care from a specialist (gastroenterologist/hepatologist) at one time.However, only approximately half (53.5%) of patients with PBC, irrespective of therapy use, were most recently treated for PBC by a specialist.
Conclusions: This is the most comprehensive and contemporary estimation of PBC prevalence in the United States to date. The pockets of high prevalence of PBC located in some rural areas highlight the need to better evaluate PBC risk factors and potential barriers in access to specialist care once patients are diagnosed. Greater awareness of PBC and its management are needed.
Keywords: epidemiology, liver disease, PBC, regional variability, specialist
Hepatology Communications - Copyright © 2025 TheAuthor(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.on behalf of the American Associationfor the Study of Liver Diseases.
Note: Obeticholic acid, marketed under the brand name Ocaliva® for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), was voluntarily withdrawn from the US market by Intercept Pharmaceuticals following a request from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 11/14/2025